Click “View in Mac App Store”. Once the App Store opens, click 'Get', then click 'Install App'. If prompted, enter your Apple ID and password. If the downloaded.rdp file opens in a program called 'Remote Desktop Connection' instead of 'Microsoft Remote Desktop', it will look like the following. Get the Remote Desktop client. Follow these steps to get started with Remote Desktop on your Mac: Download the Microsoft Remote Desktop client from the Mac App Store. Set up your PC to accept remote connections. (If you skip this step, you can't connect to your PC.) Add a Remote Desktop connection or a remote resource. For Mac users, the stalwart tool has been the Microsoft Remote Desktop connection. Available now through the Mac App store, it allows users to remotely connect to a Windows desktop to access local.
Applies To: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016
You can use the Remote Desktop client for Mac to work with Windows apps, resources, and desktops from your Mac computer. Use the following information to get started - and check out the FAQ if you have questions.
Note
- Curious about the new releases for the macOS client? Check out What's new for Remote Desktop on Mac?
- The Mac client runs on computers running macOS 10.10 and newer.
- The information in this article applies primarily to the full version of the Mac client - the version available in the Mac AppStore. Test-drive new features by downloading our preview app here: beta client release notes.
Get the Remote Desktop client
Follow these steps to get started with Remote Desktop on your Mac:
- Download the Microsoft Remote Desktop client from the Mac App Store.
- Set up your PC to accept remote connections. (If you skip this step, you can't connect to your PC.)
- Add a Remote Desktop connection or a remote resource. You use a connection to connect directly to a Windows PC and a remote resource to use a RemoteApp program, session-based desktop, or a virtual desktop published on-premises using RemoteApp and Desktop Connections. This feature is typically available in corporate environments.
What about the Mac beta client?
We're testing new features on our preview channel on AppCenter. Want to check it out? Go to Microsoft Remote Desktop for Mac and select Download. You don't need to create an account or sign into AppCenter to download the beta client.
If you already have the client, you can check for updates to ensure you have the latest version. In the beta client, select Microsoft Remote Desktop Beta at the top, and then select Check for updates.
Add a workspace
Subscribe to the feed your admin gave you to get the list of managed resources available to you on your macOS device.
To subscribe to a feed:
- Select Add feed on the main page to connect to the service and retrieve your resources.
- Enter the feed URL. This can be a URL or email address:
- This URL is usually a Windows Virtual Desktop URL. Which one you use depends on which version of Windows Virtual Desktop you're using.
- For Windows Virtual Desktop (classic), use
https://rdweb.wvd.microsoft.com/api/feeddiscovery/webfeeddiscovery.aspx. - For Windows Virtual Desktop, use
https://rdweb.wvd.microsoft.com/api/arm/feeddiscovery.
- For Windows Virtual Desktop (classic), use
- To use email, enter your email address. This tells the client to search for a URL associated with your email address if your admin configured the server that way.
- This URL is usually a Windows Virtual Desktop URL. Which one you use depends on which version of Windows Virtual Desktop you're using.
- Select Subscribe.
- Sign in with your user account when prompted.
After you've signed in, you should see a list of available resources.
Once you've subscribed to a feed, the feed's content will update automatically on a regular basis. Resources may be added, changed, or removed based on changes made by your administrator.
Export and import connections
You can export a remote desktop connection definition and use it on a different device. Remote desktops are saved in separate RDP files.
To export an RDP file:
- In the Connection Center, right-click the remote desktop.
- Select Export.
- Browse to the location where you want to save the remote desktop RDP file.
- Select OK.
To import an RDP file:
- In the menu bar, select File > Import.
- Browse to the RDP file.
- Select Open.
Add a remote resource
Remote resources are RemoteApp programs, session-based desktops, and virtual desktops published using RemoteApp and Desktop Connections.
- The URL displays the link to the RD Web Access server that gives you access to RemoteApp and Desktop Connections.
- The configured RemoteApp and Desktop Connections are listed.
To add a remote resource:
- In the Connection Center select +, and then select Add Remote Resources.
- Enter information for the remote resource:
- Feed URL - The URL of the RD Web Access server. You can also enter your corporate email account in this field – this tells the client to search for the RD Web Access Server associated with your email address.
- User name - The user name to use for the RD Web Access server you are connecting to.
- Password - The password to use for the RD Web Access server you are connecting to.
- Select Save.
Rdp For Mac Setup
The remote resources will be displayed in the Connection Center.
Connect to an RD Gateway to access internal assets
A Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) lets you connect to a remote computer on a corporate network from anywhere on the Internet. You can create and manage your gateways in the preferences of the app or while setting up a new desktop connection.
To set up a new gateway in preferences:
- In the Connection Center, select Preferences > Gateways.
- Select the + button at the bottom of the table Enter the following information:
- Server name – The name of the computer you want to use as a gateway. This can be a Windows computer name, an Internet domain name, or an IP address. You can also add port information to the server name (for example: RDGateway:443 or 10.0.0.1:443).
- User name - The user name and password to be used for the Remote Desktop gateway you are connecting to. You can also select Use connection credentials to use the same user name and password as those used for the remote desktop connection.
Manage your user accounts
When you connect to a desktop or remote resources, you can save the user accounts to select from again. You can manage your user accounts by using the Remote Desktop client.
To create a new user account:
- In the Connection Center, select Settings > Accounts.
- Select Add User Account.
- Enter the following information:
- User Name - The name of the user to save for use with a remote connection. You can enter the user name in any of the following formats: user_name, domainuser_name, or user_name@domain.com.
- Password - The password for the user you specified. Every user account that you want to save to use for remote connections needs to have a password associated with it.
- Friendly Name - If you are using the same user account with different passwords, set a friendly name to distinguish those user accounts.
- Select Save, then select Settings.
Customize your display resolution
You can specify the display resolution for the remote desktop session.
- In the Connection Center, select Preferences.
- Select Resolution.
- Select +.
- Enter a resolution height and width, and then select OK.
To delete the resolution, select it, and then select -.
Displays have separate spaces
If you're running Mac OS X 10.9 and have disabled Displays have separate spaces in Mavericks (System Preferences > Mission Control), you need to configure this setting in the Remote Desktop client using the same option.
Drive redirection for remote resources
Drive redirection is supported for remote resources, so that you can save files created with a remote application locally to your Mac. The redirected folder is always your home directory displayed as a network drive in the remote session.
Note
In order to use this feature, the administrator needs to set the appropriate settings on the server.
Use a keyboard in a remote session
Mac keyboard layouts differ from the Windows keyboard layouts.
- The Command key on the Mac keyboard equals the Windows key.
- To perform actions that use the Command button on the Mac, you will need to use the control button in Windows (for example Copy = Ctrl+C).
- The function keys can be activated in the session by pressing additionally the FN key (for example, FN+F1).
- The Alt key to the right of the space bar on the Mac keyboard equals the Alt Gr/right Alt key in Windows.
By default, the remote session will use the same keyboard locale as the OS you're running the client on. (If your Mac is running an en-us OS, that will be used for the remote sessions as well.) If the OS keyboard locale is not used, check the keyboard setting on the remote PC and change it manually. See the Remote Desktop Client FAQ for more information about keyboards and locales.
Support for Remote Desktop gateway pluggable authentication and authorization
Windows Server 2012 R2 introduced support for a new authentication method, Remote Desktop Gateway pluggable authentication and authorization, which provides more flexibility for custom authentication routines. You can now try this authentication model with the Mac client.
Important
Custom authentication and authorization models before Windows 8.1 aren't supported, although the article above discusses them.
To learn more about this feature, check out https://aka.ms/paa-sample.
Tip
Questions and comments are always welcome. However, please do NOT post a request for troubleshooting help by using the comment feature at the end of this article. Instead, go to the Remote Desktop client forum and start a new thread. Have a feature suggestion? Tell us in the client user voice forum.
See All Results For This Question
Network administrators can use this information to make sure that Mac computers and other Apple devices can connect to services such as the App Store and Apple's software-update servers.
Ports used by Apple products
This is a quick-reference guide showing common examples, not a comprehensive list of ports. This guide is updated periodically with information available at the time of publication.
Some software might use different ports and services, so it can be helpful to use port-watching software when deciding how to set up firewalls or similar access-control schemes.
Some services might use more than one of these ports. For example, a VPN service can use up to four different ports. When you find a product in this list, search (Command-F) in your browser for that name, then repeat your search (Command-G) to locate all occurrences of that product.
Some firewalls allow selective configuration of UDP or TCP ports with the same number, so it's important to know the type of port you're configuring. For example, NFS can use TCP 2049, UDP 2049, or both. If your firewall doesn't allow you to specify the type of port, configuring one type of port probably configures the other.
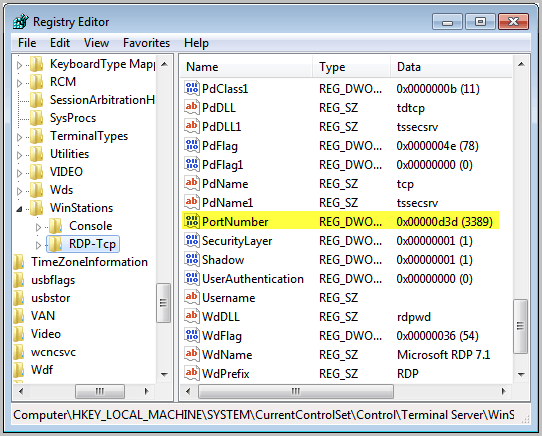
| Port | TCP or UDP | Service or protocol name1 | RFC2 | Service name3 | Used by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | TCP/UDP | echo | 792 | echo | — |
| 20 | TCP | File Transport Protocol (FTP) | 959 | ftp-data | — |
| 21 | TCP | FTP control | 959 | ftp | — |
| 22 | TCP | Secure Shell (SSH), SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), and Secure copy (scp) | 4253 | ssh | Xcode Server (hosted and remote Git+SSH; remote SVN+SSH) |
| 23 | TCP | Telnet | 854 | telnet | — |
| 25 | TCP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) | 5321 | smtp | Mail (sending email); iCloud Mail (sending email) |
| 53 | TCP/UDP | Domain Name System (DNS) | 1034 | domain | — |
| 67 | UDP | Bootstrap Protocol Server (BootP, bootps) | 951 | bootps | NetBoot via DHCP |
| 68 | UDP | Bootstrap Protocol Client (bootpc) | 951 | bootpc | NetBoot via DHCP |
| 69 | UDP | Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) | 1350 | tftp | — |
| 79 | TCP | Finger | 1288 | finger | — |
| 80 | TCP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) | 2616 | http | World Wide Web, FaceTime, iMessage, iCloud, QuickTime Installer, Maps, iTunes U, Apple Music, iTunes Store, Podcasts, Internet Radio, Software Update (OS X Lion or earlier), Mac App Store, RAID Admin, Backup, Calendar, WebDAV, Final Cut Server, AirPlay, macOS Internet Recovery, Profile Manager, Xcode Server (Xcode app, hosted and remote Git HTTP, remote SVN HTTP) |
| 88 | TCP | Kerberos | 4120 | kerberos | Kerberos, including Screen Sharing authentication |
| 106 | TCP | Password Server (unregistered use) | — | 3com-tsmux | macOS Server Password Server |
| 110 | TCP | Post Office Protocol (POP3), Authenticated Post Office Protocol (APOP) | 1939 | pop3 | Mail (receiving email) |
| 111 | TCP/UDP | Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | 1057, 1831 | sunrpc | Portmap (sunrpc) |
| 113 | TCP | Identification Protocol | 1413 | ident | — |
| 119 | TCP | Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) | 3977 | nntp | Apps that read newsgroups. |
| 123 | UDP | Network Time Protocol (NTP) | 1305 | ntp | Date & Time preferences, network time server synchronization, Apple TV network time server sync |
| 137 | UDP | Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) | — | netbios-ns | — |
| 138 | UDP | NETBIOS Datagram Service | — | netbios-dgm | Windows Datagram Service, Windows Network Neighborhood |
| 139 | TCP | Server Message Block (SMB) | — | netbios-ssn | Microsoft Windows file and print services, such as Windows Sharing in macOS |
| 143 | TCP | Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) | 3501 | imap | Mail (receiving email) |
| 161 | UDP | Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) | 1157 | snmp | — |
| 192 | UDP | OSU Network Monitoring System | — | osu-nms | AirPort Base Station PPP status or discovery (certain configurations), AirPort Admin Utility, AirPort Express Assistant |
| 311 | TCP | Secure server administration | — | asip-webadmin | Server app, Server Admin, Workgroup Manager, Server Monitor, Xsan Admin |
| 312 | TCP | Xsan administration | — | vslmp | Xsan Admin (OS X Mountain Lion v10.8 and later) |
| 389 | TCP | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) | 4511 | ldap | Apps that look up addresses, such as Mail and Address Book |
| 427 | TCP/UDP | Service Location Protocol (SLP) | 2608 | svrloc | Network Browser |
| 443 | TCP | Secure Sockets Layer (SSL or HTTPS) | 2818 | https | TLS websites, iTunes Store, Software Update (OS X Mountain Lion and later), Spotlight Suggestions, Mac App Store, Maps, FaceTime, Game Center, iCloud authentication and DAV Services (Contacts, Calendars, Bookmarks), iCloud backup and apps (Calendars, Contacts, Find My iPhone, Find My Friends, Mail, iMessage, Documents & Photo Stream), iCloud Key Value Store (KVS), iPhoto Journals, AirPlay, macOS Internet Recovery, Profile Manager, Dictation, Siri, Xcode Server (hosted and remote Git HTTPS, remote SVN HTTPS, Apple Developer registration), Push notifications (if necessary) |
| 445 | TCP | Microsoft SMB Domain Server | — | microsoft-ds | — |
| 464 | TCP/UDP | kpasswd | 3244 | kpasswd | — |
| 465 | TCP | Message Submission for Mail (Authenticated SMTP) | smtp (legacy) | Mail (sending mail) | |
| 500 | UDP | ISAKMP/IKE | 2408 | isakmp | macOS Server VPN service |
| 500 | UDP | Wi-Fi Calling | 5996 | IKEv2 | Wi-Fi Calling |
| 514 | TCP | shell | — | shell | — |
| 514 | UDP | Syslog | — | syslog | — |
| 515 | TCP | Line Printer (LPR), Line Printer Daemon (LPD) | — | printer | Printing to a network printer, Printer Sharing in macOS |
| 532 | TCP | netnews | — | netnews | — |
| 548 | TCP | Apple Filing Protocol (AFP) over TCP | — | afpovertcp | AppleShare, Personal File Sharing, Apple File Service |
| 554 | TCP/UDP | Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) | 2326 | rtsp | AirPlay, QuickTime Streaming Server (QTSS), streaming media players |
| 587 | TCP | Message Submission for Mail (Authenticated SMTP) | 4409 | submission | Mail (sending mail), iCloud Mail (SMTP authentication) |
| 600–1023 | TCP/UDP | Mac OS X RPC-based services | — | ipcserver | NetInfo |
| 623 | UDP | Lights-Out-Monitoring | — | asf-rmcp | Lights Out Monitoring (LOM) feature of Intel-based Xserve computers, Server Monitor |
| 625 | TCP | Open Directory Proxy (ODProxy) (unregistered use) | — | dec_dlm | Open Directory, Server app, Workgroup Manager; Directory Services in OS X Lion or earlier This port is registered to DEC DLM |
| 626 | TCP | AppleShare Imap Admin (ASIA) | — | asia | IMAP administration (Mac OS X Server v10.2.8 or earlier) |
| 626 | UDP | serialnumberd (unregistered use) | — | asia | Server serial number registration (Xsan, Mac OS X Server v10.3 – v10.6) |
| 631 | TCP | Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) | 2910 | ipp | macOS Printer Sharing, printing to many common printers |
| 636 | TCP | Secure LDAP | — | ldaps | — |
| 660 | TCP | Server administration | — | mac-srvr-admin | Server administration tools for Mac OS X Server v10.4 or earlier, including AppleShare IP |
| 687 | TCP | Server administration | — | asipregistry | Server administration tools for Mac OS X Server v10.6 or earlier, including AppleShare IP |
| 749 | TCP/UDP | Kerberos 5 admin/changepw | — | kerberos-adm | — |
| 985 | TCP | NetInfo Static Port | — | — | — |
| 993 | TCP | Mail IMAP SSL | — | imaps | iCloud Mail (SSL IMAP) |
| 995 | TCP/UDP | Mail POP SSL | — | pop3s | — |
| 1085 | TCP/UDP | WebObjects | — | webobjects | — |
| 1099, 8043 | TCP | Remote RMI and IIOP Access to JBOSS | — | rmiregistry | — |
| 1220 | TCP | QT Server Admin | — | qt-serveradmin | Administration of QuickTime Streaming Server |
| 1640 | TCP | Certificate Enrollment Server | — | cert-responder | Profile Manager in macOS Server 5.2 and earlier |
| 1649 | TCP | IP Failover | — | kermit | — |
| 1701 | UDP | L2TP | — | l2f | macOS Server VPN service |
| 1723 | TCP | PPTP | — | pptp | macOS Server VPN service |
| 1900 | UDP | SSDP | — | ssdp | Bonjour |
| 2049 | TCP/UDP | Network File System (NFS) (version 3 and 4) | 3530 | nfsd | — |
| 2195 | TCP | Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) | — | — | Push notifications |
| 2196 | TCP | Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) | — | — | Feedback service |
| 2197 | TCP | Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) | — | — | Push notifications |
| 2336 | TCP | Mobile account sync | — | appleugcontrol | Home directory synchronization |
| 3004 | TCP | iSync | — | csoftragent | — |
| 3031 | TCP/UDP | Remote AppleEvents | — | eppc | Program Linking, Remote Apple Events |
| 3283 | TCP/UDP | Net Assistant | — | net-assistant | Apple Remote Desktop 2.0 or later (Reporting feature), Classroom app (command channel) |
| 3284 | TCP/UDP | Net Assistant | — | net-assistant | Classroom app (document sharing) |
| 3306 | TCP | MySQL | — | mysql | — |
| 3478–3497 | UDP | — | — | nat-stun-port - ipether232port | FaceTime, Game Center |
| 3632 | TCP | Distributed compiler | — | distcc | — |
| 3659 | TCP/UDP | Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) | — | apple-sasl | macOS Server Password Server |
| 3689 | TCP | Digital Audio Access Protocol (DAAP) | — | daap | iTunes Music Sharing, AirPlay |
| 3690 | TCP/UDP | Subversion | — | svn | Xcode Server (anonymous remote SVN) |
| 4111 | TCP | XGrid | — | xgrid | — |
| 4398 | UDP | — | — | — | Game Center |
| 4488 | TCP | Apple Wide Area Connectivity Service | awacs-ice | ||
| 4500 | UDP | IPsec NAT Traversal | 4306 | ipsec-msft | macOS Server VPN service |
| 4500 | UDP | Wi-Fi Calling | 5996 | IKEv2 | Wi-Fi Calling |
| 5003 | TCP | FileMaker - name binding and transport | — | fmpro-internal | — |
| 5009 | TCP | (unregistered use) | — | winfs | AirPort Utility, AirPort Express Assistant |
| 5100 | TCP | — | — | socalia | macOS camera and scanner sharing |
| 5222 | TCP | XMPP (Jabber) | 3920 | jabber-client | Jabber messages |
| 5223 | TCP | Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) | — | — | iCloud DAV Services (Contacts, Calendars, Bookmarks), Push Notifications, FaceTime, iMessage, Game Center, Photo Stream |
| 5228 | TCP | — | — | — | Spotlight Suggestions, Siri |
| 5297 | TCP | — | — | — | Messages (local traffic) |
| 5350 | UDP | NAT Port Mapping Protocol Announcements | — | — | Bonjour |
| 5351 | UDP | NAT Port Mapping Protocol | — | nat-pmp | Bonjour |
| 5353 | UDP | Multicast DNS (MDNS) | 3927 | mdns | Bonjour, AirPlay, Home Sharing, Printer Discovery |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | — | postgresql | Can be enabled manually in OS X Lion Server (previously enabled by default for ARD 2.0 Database) |
| 5897–5898 | UDP | (unregistered use) | — | — | xrdiags |
| 5900 | TCP | Virtual Network Computing (VNC) (unregistered use) | — | vnc-server | Apple Remote Desktop 2.0 or later (Observe/Control feature) Screen Sharing (Mac OS X 10.5 or later) |
| 5988 | TCP | WBEM HTTP | — | wbem-http | Apple Remote Desktop 2.x See also dmtf.org/standards/wbem. |
| 6970–9999 | UDP | — | — | — | QuickTime Streaming Server |
| 7070 | TCP | RTSP (unregistered use), Automatic Router Configuration Protocol (ARCP) | — | arcp | QuickTime Streaming Server (RTSP) |
| 7070 | UDP | RTSP alternate | — | arcp | QuickTime Streaming Server |
| 8000–8999 | TCP | — | — | irdmi | Web service, iTunes Radio streams |
| 8005 | TCP | Tomcat remote shutdown | — | — | — |
| 8008 | TCP | iCal service | — | http-alt | Mac OS X Server v10.5 or later |
| 8080 | TCP | Alternate port for Apache web service | — | http-alt | Also JBOSS HTTP in Mac OS X Server 10.4 or earlier |
| 8085–8087 | TCP | Wiki service | — | — | Mac OS X Server v10.5 or later |
| 8088 | TCP | Software Update service | — | radan-http | Mac OS X Server v10.4 or later |
| 8089 | TCP | Web email rules | — | — | Mac OS X Server v10.6 or later |
| 8096 | TCP | Web Password Reset | — | — | Mac OS X Server v10.6.3 or later |
| 8170 | TCP | HTTPS (web service/site) | — | — | Podcast Capture/podcast CLI |
| 8171 | TCP | HTTP (web service/site) | — | — | Podcast Capture/podcast CLI |
| 8175 | TCP | Pcast Tunnel | — | — | pcastagentd (such as for control operations and camera) |
| 8443 | TCP | iCal service (SSL) | — | pcsync-https | Mac OS X Server v10.5 or later (JBOSS HTTPS in Mac OS X Server 10.4 or earlier) |
| 8800 | TCP | Address Book service | — | sunwebadmin | Mac OS X Server v10.6 or later |
| 8843 | TCP | Address Book service (SSL) | — | — | Mac OS X Server v10.6 or later |
| 8821, 8826 | TCP | Stored | — | — | Final Cut Server |
| 8891 | TCP | ldsd | — | — | Final Cut Server (data transfers) |
| 9006 | TCP | Tomcat standalone | — | — | Mac OS X Server v10.6 or earlier |
| 9100 | TCP | Printing | — | — | Printing to certain network printers |
| 9418 | TCP/UDP | git pack transfer | — | git | Xcode Server (remote git) |
| 10548 | TCP | Apple Document Sharing Service | — | serverdocs | macOS Server iOS file sharing |
| 11211 | — | memcached (unregistered use) | — | — | Calendar Server |
| 16080 | TCP | — | — | — | Web service with performance cache |
| 16384–16403 | UDP | Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP), Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP) | — | connected, — | Messages (Audio RTP, RTCP; Video RTP, RTCP) |
| 16384–16387 | UDP | Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP), Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP) | — | connected, — | FaceTime, Game Center |
| 16393–16402 | UDP | Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP), Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP) | — | — | FaceTime, Game Center |
| 16403–16472 | UDP | Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP), Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP) | — | — | Game Center |
| 24000–24999 | TCP | — | — | med-ltp | Web service with performance cache |
| 42000–42999 | TCP | — | — | — | iTunes Radio streams |
| 49152–65535 | TCP | Xsan | — | — | Xsan Filesystem Access |
| 49152– 65535 | UDP | — | — | — | |
| 50003 | — | FileMaker server service | — | — | — |
| 50006 | — | FileMaker helper service | — | — | — |
1. The service registered with the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, except where noted as “unregistered use.”
2. The number of a Request for Comment (RFC) document that defines the service or protocol. RFC documents are maintained by RFC Editor.
3. In the output of Terminal commands, the port number might be replaced by this Service Name, which is the label listed in /etc/services.
FaceTime is not available in all countries or regions.
Learn more
The application firewall in macOS is not a port-based firewall. It controls access by app, instead of by port.
